HEALTH AND SAFETY AT WORK: BASIC CONCEPTS
As is evident, I will begin by defining what health is.
- Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absece of disease or infirmity (WHO - OMS).
In the same way, we have the following aspects:
- Work.
- Occupational risk.
- Work condition.

What is Health & Safety at work?
A group of measures taken in order to prevent or reduce occupational risks and improve working conditions.

It is important to discard the occupational risk factors, which are divided into 4 groups:
- Safety conditions:
- Workplaces.
- Work equipment.
- Electrical hazards and fire hazard.
- Environmental conditions:
- Physical agents.
- Chemical agents.
- Biological agents.
- Ergonomic conditions:
- Physical workload.
- Mental workload.
- Phychosocial conditions:
- Work organization.
- Personal traits.
The worker's health damages is an aspect of special importance that every person must know.
For this reason, I release the following information in a schematic way:
According to the General Law of Social Security (LGSS), an work accident is any bodily injury suffered by the worker because of or as a consequence of working for others.
Therefore, there are 3 requirements for it to be considered an work accident:
- Physical or psychic injuries.
- Working for others/hired-hand workers. Self-empoyment workers are also included if they contribute to Social Security for work accidents.
- Cause and effect reation between work and accident.
It can also be said that there are cases aasimilated by law, which are situations that might cause misunderstanding, but, since they are included in legislation, it is clear that they are work accidents.
- In itinere accidents → when going to work or going back home from work. Without interruptions, usual itinerary and an adequate means of transport.
- Trade union office → when doing union work.
- Tasks no related or different → when doing tasks not/different to the worker's professional group.
- Rescue actions → when performing rescue actions if they are connected to work.
- Occupational diseases → when contracting a disease at work not included in the list of occupational diseases and ir is proved in Court that, in fact, it was contracted at work.
- Accident consequences → accident consequences or complications that worsen the previous situations.
There are other accidents considered as work accidents:
- In mission accidents.
- Accidents caused by professional negligence.
On the other hand, not considered as work accidents:
- Force majeure accidents.
- Reckless endangerment or deceit accidents.
Still it is possible to indicate the types of accidents that we can find, and these are the following:
With personal injuries
|
Without personal injuries
|
|
With material damages
|
Material damages + personal injuries.
(Accidente típico)
|
Material damages, but no personal injuries.
(Accidente blanco)
|
Without
material damages
|
Without material damages, but with personal injuries. (Accidente caso).
|
Without material damages + Without personal injuries.
(Incidente) (Risk situation).
|
What has been said so far assumes that all accidents occur due to a cause. This cause could have been avoided and, therefore the accident too.
Therefore, we find 2 types of causes:
- Technical causes.
- Human causes.
However, within this section, there are also occupational diseases, which are classified as follows:
Now, I will address the main differences that exist between an work accident and occupational diseases. In a brief and specific way:
- Work accident
- Quick
- Reated to safety conditions
- Identical effects
- Occupational disease
- Slow.
- Related to environmental conditions.
- Individual effects.
And, last but not least, I will emphasize the main measures of prevention and protection that every worker must keep in mind and know at all times.
- Prevention measures
- machinary and chemical substitution.
- repairs and maintenance.
- equipment initial design.
- Protection measures
- Collective protection
- banisters or railings and safety nets.
- machinery safety guards.
- noise shields.
- Individual protection → worker
- masks, gloves, boots, earplugs, noise eaarmuffs, etc.
- Health and Safety disciplines → This part, I will explain it to you by means of examples that have arisen to some workers or, simply, cases that can arise to you.
- Safety at work
- To design safe guards for electrical tools.
- Occupational or Industrial Hygiene
- To do environmental pollutants measurings, analyze them, and evaluate the exposure dose.
- Ergonomics
- To choose comfortable chairs and desks.
- Psychosociology
- To organize work using task rotation to avoid monotony.
- Occupational medicine
- To do annual check-ups.
HEALTH AND SAFETY AT WORK: LEGISLATION AND ORGANIZATION
As the title rightly says. I will talk about occupational health and safety legislation. The legal framework of this section is divided into four levels, which are the following:
- International standards.
- Spanish Consitution → In according with the article 40.2, Public Authorities must look after worker's health and safety.
- Basic legislation
- Occupational Risks Prevention Act 31/1995 of 8th November.
- Reguations for Prevention Services RD 39/1997 of 17th January.
- Specific legisation.
After what has been said above, we have to take into account the duties in Occupational Heath and Safety:
DUTIES IN
OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH & SAFETY
|
|
EMPLOYERS DUTIES
|
WORKERS DUTIES
|
Implementing and
applying an occupational risk prevention plan.
|
Using properly:
· PPE.
· Machines.
· Tools.
· Not putting out of operation safety devices.
|
Assessing
occupational risks when they can’t be avoided.
|
|
Providing personal
protective equipment (PPE –EPls).
|
|
Preparing an emergency
plan including.
|
Informing immediately
superiors or safety representatives of risk situations.
|
Adopting measures in
case of serious and imminent danger.
|
|
Informing and
training.
|
|
Consultation and
participation.
|
Cooperating with the
employer in Occupational Health and Safety issues.
|
Health surveillance.
|
|
Maternity and
breastfeeding protection.
|
|
Protection of
special risk groups.
|
|

Now, we are going to focus on the liabilities in occupational heath and safety issues.
From my point of view, I'm going to divide it into three sections, so that it reflects well and you can understand it.
So, let's start:
- Empoyer
- Offences in occupational health and safety issues involve a penalty.
- Types of responsability:
- Administrative liability.
- Public liability.
- Criminal liability.
- Surchage on Social Security benefits.
- Workers → App, they can be punished by the employer.
- Minor, major, and serious misconducts: collective bargaining agreement.
- Labour Inspection Role → Institution that supervises the compliance of labour and occupational health and safety law.
As for the occupational health and safety organization, employers must plan and organize health and safety at work.
In this way, they are classified into different types, which I will briefly develop, making known the most relevant aspects:
- Personally assuming prevention activities
- Companies with less than 25 employees and just one workplace. Employers must have basic level training as well.
- Appointing one or several workers to carry prevention activities out.
- The employer names one or several workers to manage health and safety at work.
- Establishing an internal prevention service
- Companies with more than 500 workers.
- Companies between 250-500 workers + special risk activities.
- Version → Joint prevention services.
- Contracting an external prevention service.
In the same way, we are going to delve into the worker's health, that is, workers' participation in occupational health and safety.
- Safety representatives
- designated by and among workers' representatives.
- Health and Safety Committee
- Companies with 50 workers and workers council.
- All members must have a basic level training in health and safety at work.
- Competences and Powers:
- Being consulted
- Participating in the occupational risk prevention plan.
- Having acess to occupational health and safety documents.
- Accompanying Labour Inspection.
The next section deals with occupational health and safety management.
In this section, I wil cite some of the generic principles of action. I highlight the following:
- Avoiding risks.
- Replacing dangerous equipment, tools, chemicals, etc. by non-dangerous or ess dangerous ones.
- Giving appropiate instructions to workers.
- Job-person adaptation.
Most workers will ask "how to assess if there are not occupational risks?", well, there is the occupational risks assessment.
To assess occupationa risks, we can use the INSHT risk assessment method, which is the following:
Consequences or severity
|
||||
Slightly harmful
(cuts, headaches)
|
Harmful
(burns, deafness, asthma)
|
Extremely harmful
(amputations, intoxications,
fatal accidents)
|
||
Probability |
Low
(rarely, hardly ever)
|
Trivial (T)
|
Tolerable (To)
|
Moderate (Mo)
|
Medium
(occasionally)
|
Tolerable (To)
|
Moderate (Mo)
|
Important (I)
|
|
High
(always, nearly always)
|
Moderate (Mo)
|
Important (I)
|
Intolerable (In)
|
|
- Trivial: specific actions are not necessary.
- Tolerable: prevention measures don't need to be improved. Regular checks.
- Moderate: efforts to reduce the risk should be made.
- Important: work shouldn't start until the risk has been reduced
- Intolerable: work shouldn't start or continue until the risk has been reduced.
Within the working accidents management we can find two types of accidents:
- Accidents investigation: accidents to investigate (INSHT)
- Accidents record and notification.
To sum up with this section, I wil mention the two types of accidents costs that exist and explained in a global way:
- Costs for companies
- Salaries and compensations to workers.
- Downtime in helping the victim.
- Image loss.
- Costs for the worker and for society:
- For the worker and her/his society
- For society
HEALTH AND SAFETY AT WORK: OCCUPATIONAL RISKS FACTORS AND THEIR PREVENTION
Previously, I made known in general terms the occupational risk factors that could appear at work.
Next, I will delve into each one of them and the prevention and protection measures necessary to face it.
As a review, we recover the general picture of risk factors, as well as add the general damages associated with each one:
Next, I will delve into each one of them and the prevention and protection measures necessary to face it.
As a review, we recover the general picture of risk factors, as well as add the general damages associated with each one:
Safety Conditions
|
· workplaces
· work equipment
· Electrical hazard and fire hazard.
|
Working accidents
|
Environmental
Conditions
|
· psysical agents
· chemical agents
· biogical agents
|
Occupational diseases
|
Ergonomic
Conditions
|
· psysical workload
· mental workload
|
· psysical fatigue
· mental fatigue
|
Psychosocial
Conditions
|
· work organization
· personal traits
|
· job dissatisfaction
· stress
· mobbing
· burnout
|
Now, I'm going to focus on safety conditions: occupational risk factors, especially in four types:
- Workplaces: RD 486/1997 Safety and health at workplaces.
- Workplace: industrial facilities, patways, break and first aid posts.
- Damages: slips, falls of people, etc.
- Machines and tools
- Machinery: one of the main occupational risks in working accidents. It usually causes serious personal injuries
- Tools: they cause frequent working accidents, but with minor consequences.
- Electrical hazards: They are 2 ways:
- Direct contact
- Indirect contact
- High-votage contacts
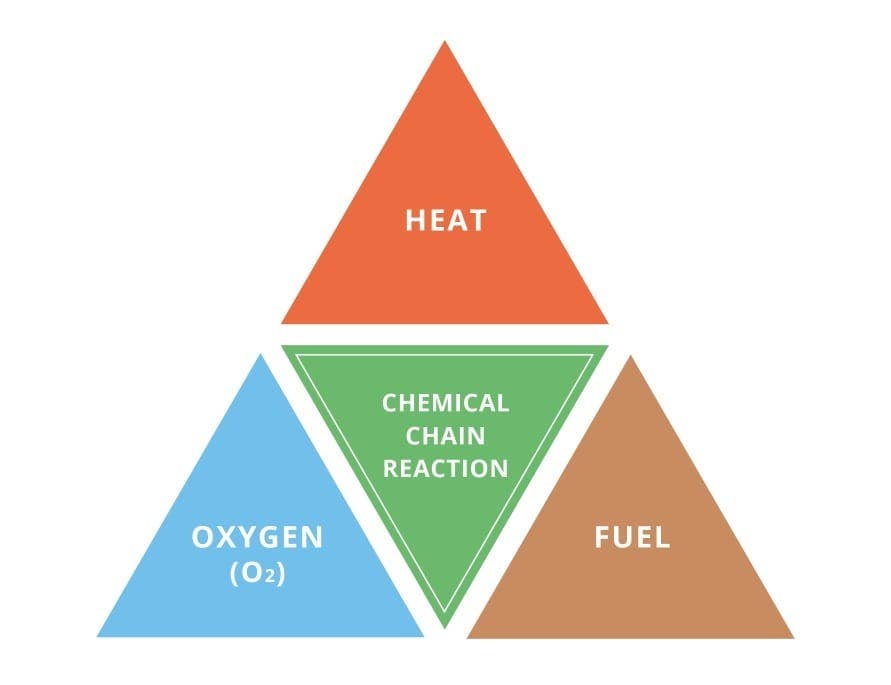
- Fire tetrahedron
- Fuel
- Oxidizing agent
- Heat
- Chain reaction
- Classes of fires
- Class A: solids.
- Cass B: liquids.
- Class C: gases.
- Class D: metals.
The 2 types of most significant extinguishers are:
- Multipurpose dry chemical (ABC).
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Similarly, we find the environmental conditions: occupational factors.
I'll start with the psycical agents:
- Noise
- Unwanted or damaging sound. It is measured in decibels.
- 87 dB (A-weighted) over an 8hour period and a peal level of 140 dB (C-weighted).
- Types:
- Continuous noise
- Intermittent noise
- Impulsive or impact noise
- Prevention/Protection measures
- Technical and organizational measures
- Noise assessment: >80dB (every 3 years); >85dB (yearly)
- Medical chek-ups: >80dB (every 5 years); >85dB (every 3 years).
- Measures on workers
- Vibrations
- Types:
- hand-arm vibration
- whole-body vibration
- Radiation
- Types:
- Ionizing radiation (the most dangerous)
- Non-ionizing radiation (the least dangerous)
- Temperature
- Human body needs a temperature of 37ºC
- Damage:
- because of excessive heat
- heat stroke
- fainting, heat exhaustion
- Because of excessive cold
- hypothermia: temperature below 35ºC
- Lighting
- measure unit: lux (lx).
- prevention/protection measures
- using natural light.
- having general and localized ilumination.
- avoiding contrasts and dazzles.
- Chemical agents
- Types
- Solids
- Liquids
- Gases
- Damages
- Irritant
- Corrosive
- Suffocating
- Anaesthetic
- Sensitizing
- Carcinogen and mutuagenic
- Pneumoconiotic
- Systemic
- Prevention/Protection measures
- Occupational or Industrial Hygiene → Health and Safety discipline
- Biological agents
- Ways of entering the human body: through respiratory system, digestive system, through skin or injuries.
- Risk group classification
- Group 1: it is unlikely to cause human disease.
- Group 2: can cause human disease and might be a hazard to workers, It is unlikely to spread to the community.
- Group 3: can cause severe human disease and a serious hazard to workers.
- Group 4: cause severe human disease and a serious hazard to workers. High risk of spreading to the community.
- Prevention/Protection measures:
- vaccines and regular medical check-ups.
- suitable hygienic conditions.
- Physical workload
- Workload
- physical demands → physical workload
- mental demands
- Physical workload
- Physical efforts and repetitive movements
- Incorrect or poor postures
- Manual load handling >3 kgs. Maximum load: 25 kgs.
- Mental workload: can cause mental fatigue.
As we all know, the use of computers has caused the appearance of new occupational risks for most workers.
Its most obvious and prominent damages are:
- Visual fatigue fatiga visual
- Muscular fatigue
- Headaches, insommia...
Prevention/Protection measures:
- taking breaks.
- medical chech-ups.
- information and training.
To conclude this section I am going to make known the psychosocial conditions, that is, occupational risks factors.
In psychosocial conditions interact:
- company's characteristcs.
- worker's characteristics.
- Job dissatisfaction.
- Occupational burnout.
- Work stress.
- Harassment at work.



No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario